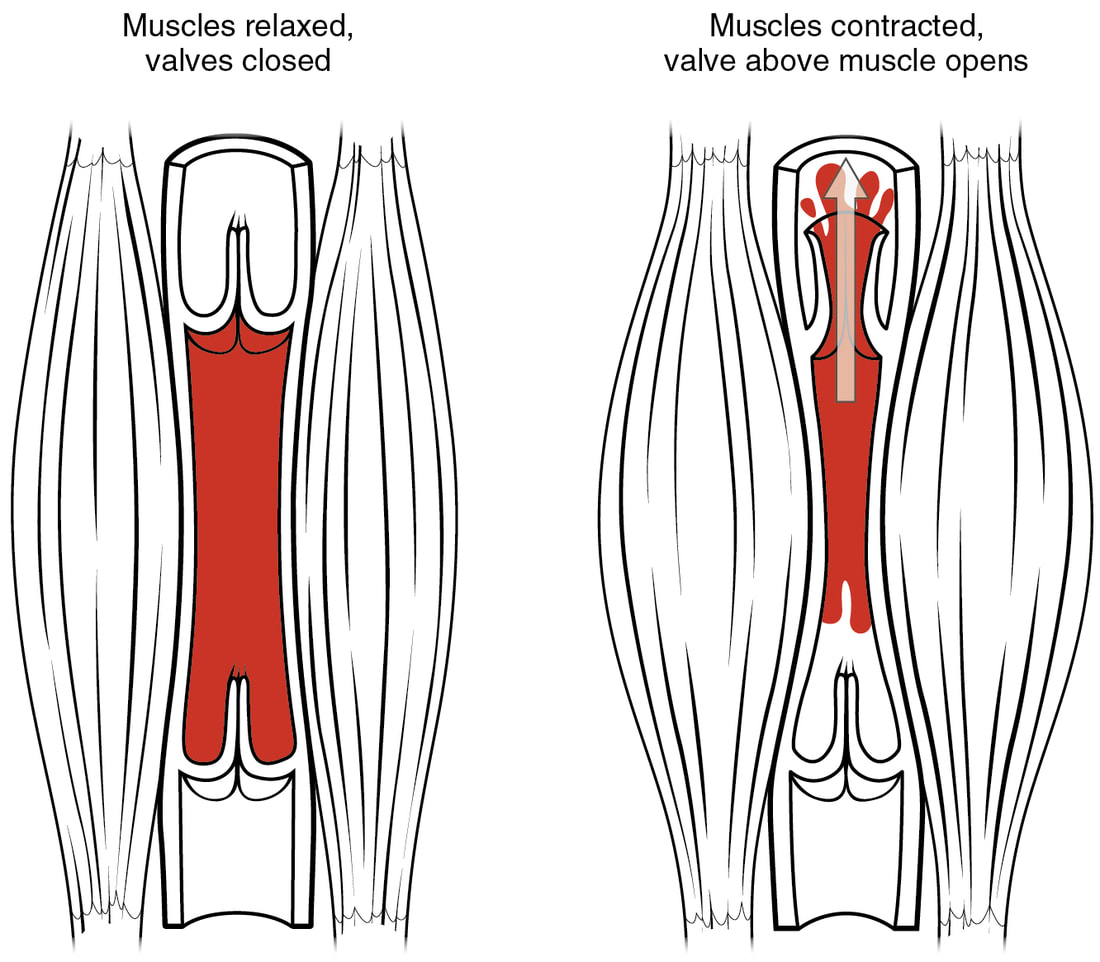
Series 4 - MassageMassage is defined as the systematic manipulation of the soft tissues of the body. Therapeutic Effects of Massage Mechanical Responses Occur as a direct result of the graded pressures and movements of the hand on the body. Massage encourages venous and lymphatic drainage as well a mild stretch of superficial and scar tissue. Stagnation of circulation due to inactivity can be prevented by using massage therapy techniques. Physiological Responses Massage can increase metabolism to the musculature and aid in the removal of metabolites. It also helps overcome venostasis and edema by increasing circulation at and around the injury site. Reflex effects of massage elicit a variety of organ reactions such as body relaxation, stimulation and increased circulation. Relaxation is beneficial for tense, anxious clients who may require a gentle treatment. Stimulation benefits are primarily psychological and is relatively ineffectual physiologically. Increased circulation by massage is caused by the capillaries dilating and the fluid being drained as a result of firm outside pressure. This stimulates cell metabolism, eliminating toxins and increases lymphatic and venous circulation. Psychological Responses The tactile system is one of the most sensitive systems in the human organism. Because massage is the act of laying on of hands, it can be an important means for creating a bond of confidence between the athletic trainer and the athlete. References: Arnheim’s Principles of Athletic Training - A Competency Based Approach, William E. Prentice, 12 Edition, 2006, pg 421-426
0 Comments
Series 3 - TENS Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulators
Pain ModulationMuscle ContractionReferences
Arnheim’s Principles of Athletic Training - A Competency Based Approach, William E. Prentice, 12 Edition, 2006, pg 416-420 Upcoming - Series 4 - Massage Series 2 - Therapeutic UltrasoundWhat Is Ultrasound? Ultrasound is defined as inaudible acoustic vibrations that may produce either thermal or nonthermal physiological effects. When sound scatters and absorbs as it penetrates the tissue, its energy is decreased. Equipment The main piece of equipment for delivering therapeutic ultrasound is a high-frequency generator, which provides an electrical current through a coaxial cable to a transducer contained within an applicator. The crystals in the head of the applicator expand and contract producing oscillations at the same frequency as sound waves. Indications - Thermal Effects
Indications - Non-Thermal Effects.
Application Acute injuries require more frequent treatments over a shorter period of time Chronic conditions require fewer treatments over a longer period of time Ultrasound should begin as soon as possible after injury to maximize effects on the healing process. Acute conditions may require treatment once daily for 6-8 days. Chronic conditions can be used on alternating days for 10-12 treatments. References Arnheim’s Principles of Athletic Training - A Competency Based Approach, William E. Prentice, 12 Edition, 2006, pg 412-415 We offer ultrasound. Book an Athletic Therapy appointment today to determine if ultrasound should be included in your therapeutic treatment.
What does the Science say?
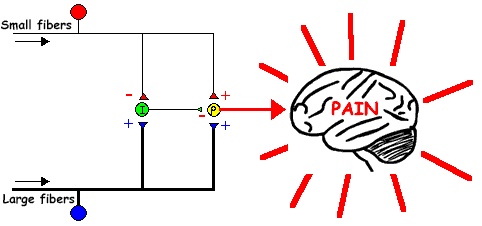
The research appears to be limited in regards to documenting the benefits of therapeutic cupping. Although the treatment has been around for centuries there is limited scientific research on the cause and effect of cupping. The below article helped outline a number of studies. I have compiled some of the research into a short review. The Medical Perspective of Cupping Therapy: Effects and Mechanisms of Action, Abdullah M.N et.al. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 2019, pg 90-97 The main motivation for this review as outlined by the authors is the controversial premise that cupping is based on a placebo effect and has no actual therapeutic results. The purpose of the authors review was to determine the mechanisms of action and explain the effects cupping has as a therapeutic treatment in modern medicine. The authors reviewed 64 articles that focused on explaining the mechanisms of cupping using the scientific method. With these articles the authors discovered found scientific evidence that there is an increase in opioid production in the brain leading to both pain control and relaxation. Other studies reviewed looked at improved circulation of cupping and how this promotes toxin removal from the body. Three theories and hypotheses were discussed for cupping as a treatment option in the reduction of pain. These theories and hypotheses included the Gate Control Theory, Diffuse of Noxious Inhibitory Controls, Reflex Zone Theory, Release of Nitric Oxide Theory, Activation of Immune System Theory, and Blood Detoxification Theory. For my review I decided to include conclusions based on the first 4 theories. The Gate Control Theory This theory is based on a study performed in 1965, whereby scientist hypothesized that there are both thin and thick neural pathways from an injury site to the central nervous system. These pathways carry information such as temperature, pressure and pain however the thicker neural pathways are believed to inhibit the thinner pathways of pain. It is believed that cupping activates that thicker inhibitory pathways of pain and therefore reduces that individuals perception of pain. The authors point out that the extent cupping impacts this pathway is unknown and more research is required in this area. Diffuse of Noxious Inhibitory Controls This theory is based on an idea that you can only register one pain signal at a time from an injury site. This means that by creating discomfort with the cups you can override that original pain signal. This action is similar to acupuncture where the local area is triggered by the new pain creating a “pain inhibits pain” effect. Reflex Zone Theory This theory basis its premise on the link between different areas of the body. That there exists a link between nerves muscle and skin. The hypotheses suggests that cupping an area of the body will impact another area of the body via the neural pathways they share. Organs that are diseased have been known to show up as sign and symptoms in other areas of the body. The authors do point out that more research is needed into this theory to get a better understanding of the exact mechanism being impacted with cupping. Release of Nitric Oxide Theory Nitric oxide is an important vasodilator that regulates both blood flow and volume and has been associated with collagen formation and strength at an injury site. Studies have shown an increase in Nitric oxide in tissue post cupping. Conclusion According to the authors of this review no single theory could explain all the benefits of therapeutic cupping. It’s important to note that larger randomized test need to performed to understand the scientific benefits of cupping in modern science. Curious if cupping would be a beneficial addition to your therapeutic treatment. Add cupping for free to your 60 or 90 minute massage therapy treatment for the month of September. Upcoming - Series 2 - Ultrasound - What is Therapeutic Ultrasound? Over the next couple weeks we will dive into why therapists utilize therapeutic modalities during treatment? How these modalities could be beneficial to your rehab and when they are the most effective during treatment?We start off the series understanding myofascial cupping. Series 1 - Myofascial CuppingIt is important to stress that this is not a exhaustive list of contraindications for cupping and when seeking new treatment modalities it is important you receive direction from a certified therapist or health care provider. The basic rule for cupping techniques is to use common sense when determining if an area should be cupped. In general if an area is safe to massage in theory you should also be able to use cups. For practitioners trained in the use of cupping it is important to note that the skill level or competency of the individual practitioner plays a role in whether or not an area can be treated. Below is a list of contraindications for cupping: - malignant tumours - acute musculoskeletal injuries - low blood pressure or other acute circulatory conditions - superficial blood vessels e.g. inside forearm, anterior neck, varicose veins - cupping during pregnancy should be cupped gently in specific areas - elderly and children should be cupped gently - diabetes and medicated for blood thinning - duration should not exceed 10 minute for a stationary cup - light cupping shoulder be used over the spine depending on the mass of the tissue - herniated and bulging discs should not have stationary cups on the spinous processes - extreme cold - open wounds - acute rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia, automimmune - healing fractures - hypersensitivity of the skin - anuerysm - haematoma - sutures - acute venous disease - high temperature - deep vein thrombosis (DVT) - infectious disease Cupping Applications and Benefit
Next week we will review some of the scientific literature on cupping…. Curious if cupping would be a beneficial addition to your therapeutic treatment. Add cupping for free to your 60 or 90 minute massage therapy treatment for the month of September. Over the next couple weeks we will dive into why therapists utilize therapeutic modalities during treatment? How these modalities could be beneficial to your rehab and when they are the most effective during treatment? We start off the series understanding myofascial cupping. Series 1 - Myofascial CuppingWhat is Myofascial Cupping?Cupping has been used for Centuries but more recently was made popular by professional athletes. Cupping refers to the application of domed cups applied to the skin and removal of the air within the cup to create a suction. This is often done by drawing the air out but can also be removed with heat. As the cups are applied the skin is pulled into the cup and the cup is held in place.
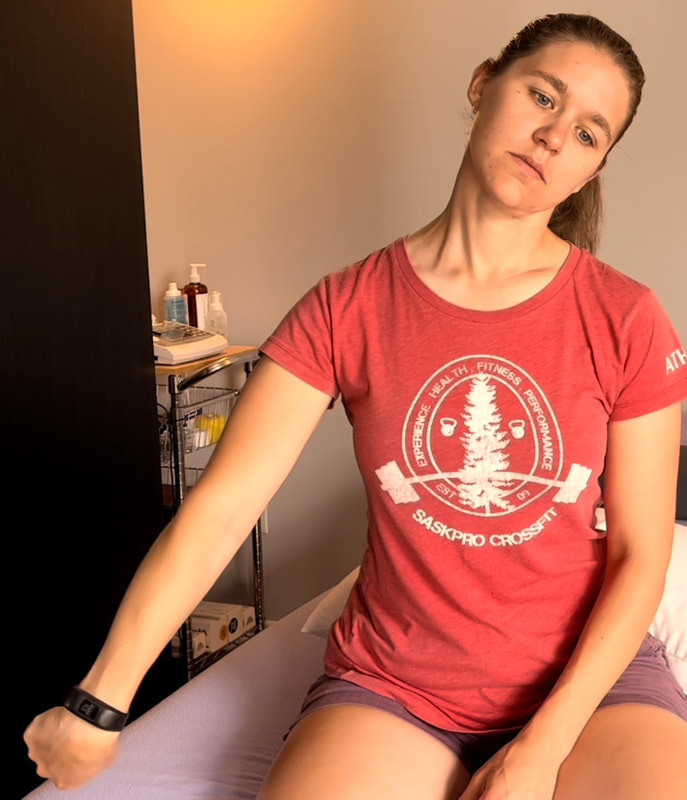
Cupping mimics a number of manual treatment techniques utilized by therapists that include pinching, rolling and tool scraping. The intensity of the cupping can vary and often the technique of cupping is individualized to the treating therapist. History of CuppingCupping has been recorded to have started in 281-341 A.D by an Ge Hong, a Taoist alchemist and herbalist. This initial form of cupping was used for draining wounds and originally used animal horns. Later the Chinese Dynasty would use this application in therapeutic treatment of headaches, dizziness, and abdominal pain. Cups were made of pottery or bamboo and were used for both cold and hot applications. The cups would be applied to the skin over acupuncture needles. Today’s cupping utilizes glass, plastic, or silicone cups. These cups were an improvement on the previous types as they were less likely to break and you are able to view the skin under the cup during treatment. Glass cups use fire to remove the air with-in the cup. The cups interior is rubbed with alcohol then set a light before being placed onto the skin. Silicone cups are depressurized by pressing down onto the top of the dome and plastic cups have a vacuum attachment to remove the air. Next week we will cover the contraindications of cupping as well as the health benefits…. Curious if cupping would be a beneficial addition to your therapeutic treatment. Book an appointment today! NOTE: Please seek a professional diagnosis and discontinue the tests suggested if you have an increase in symptoms. This is only meant as a guide. We do not diagnosis. Are you suffering from numbness and tingling in your hands and fingers? Do you have general aches in your shoulder, elbow or wrist? This discomfort is often intermittent or moves around. You could describe the pain like a tooth ache but you don’t find that the site itself is tender to the touch. Do you suffer from chronic neck and upper back tightness? You could have a nerve impingement, tension or entrapment. Often times neural tension is diagnosed as carpal tunnel syndrome, tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, or shoulder impingement. If you have been receiving treatment for any of these but have not been getting the results you want try this simple test at home to find out if you have neural tension. Start with an Upper Limb Tension Test. Follow the step by step guide to help determine if could benefit from neural tension treatment as part of your health and fitness routine. Book an Athletic Therapy or Massage Therapy appointment today if you would like to be walked through this testing and receive treatment. Upper Limb Tension Test # 1 - Median Nerve TestBe sure to be sitting upright and comfortable. Bring the right ear towards the right shoulder. Be sure to only have a light stretch in the neck. There should be no pinching in the neck. If there is you have gone to far into the stretch. Bring the left arm up to shoulder height. Extend at the left wrist and fingers. Slowly extend the left arm back maintaining the left hand at shoulder height. Stop movement when you start to feel a stretch. Try on the opposite side. Compare right and left. You could feel tension anywhere between the left shoulder to the left finger tips but is most commonly felt at the elbow, wrist or middle finger.
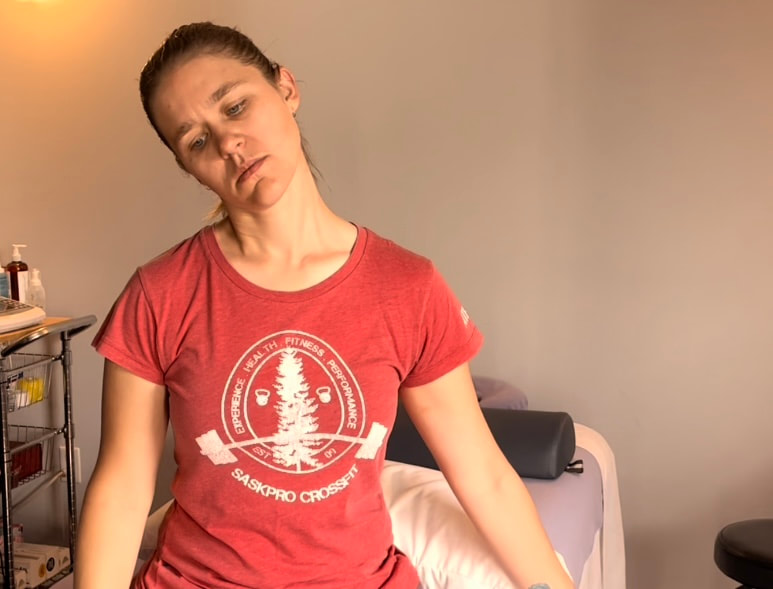
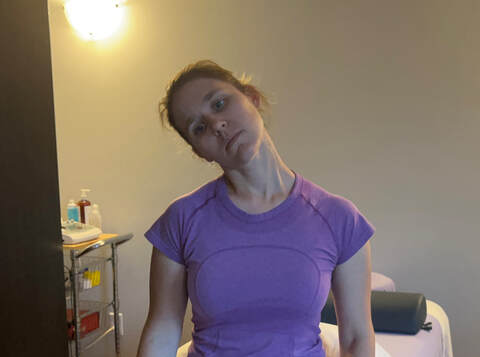
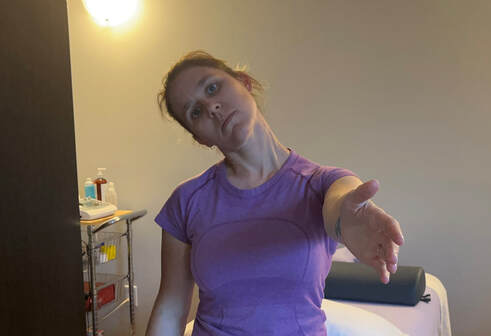
If you tested positive with the nerve tension test….NOW WHAT… Good news you can work on improving neural tension the same way you can work on mobility of a joint or flexibility of a muscle. Check out our YouTube Channel to view our new nerve flossing videos to improve neural tension or book an appointment and receive an in person treatment or virtual guidance. NOTE: Please seek a professional diagnosis and discontinue the tests suggested if you have an increase in symptoms. This is only meant as a guide. We do not diagnosis. Are you suffering from numbness and tingling in your hands and fingers? Do you have general aches in your shoulder, elbow or wrist? This discomfort is often intermittent or moves around. You could describe the pain like a tooth ache but you don’t find that the site itself is tender to the touch. Do you suffer from chronic neck and upper back tightness? You could have a nerve impingement, tension or entrapment. Often times neural tension is diagnosed as carpal tunnel syndrome, tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, or shoulder impingement. If you have been receiving treatment for any of these but have not been getting the results you want try this simple test at home to find out if you have neural tension. Start with an Upper Limb Tension Test. Follow the step by step guide to help determine if could benefit from neural tension treatment as part of your health and fitness routine. Book an Athletic Therapy or Massage Therapy appointment today if you would like to be walked through this testing and receive treatment. Upper Limb Tension Test # 2 - Radial Nerve Test
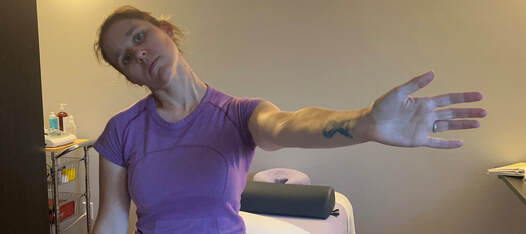
2. Bring your arm forward and rotate the wrist so your palm is facing back. Flex at the wrist 3. Bring your arm forward and rotate the wrist so your palm is facing back. Flex at the wrist 4. Try on the opposite side. Compare right and left. You could feel tension anywhere between your shoulder and fingers. Tension is usually felt at the back of the hand/wrist or outside elbow.
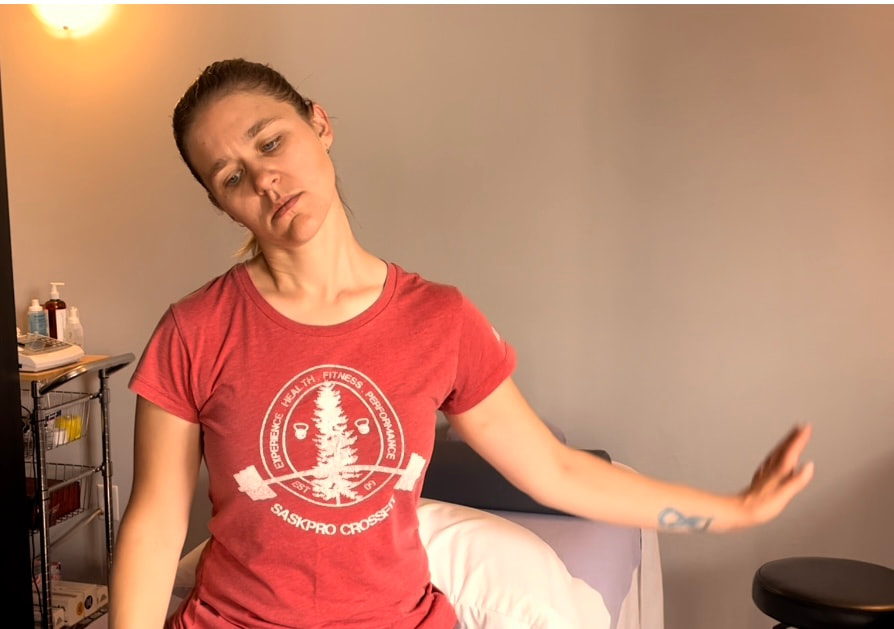
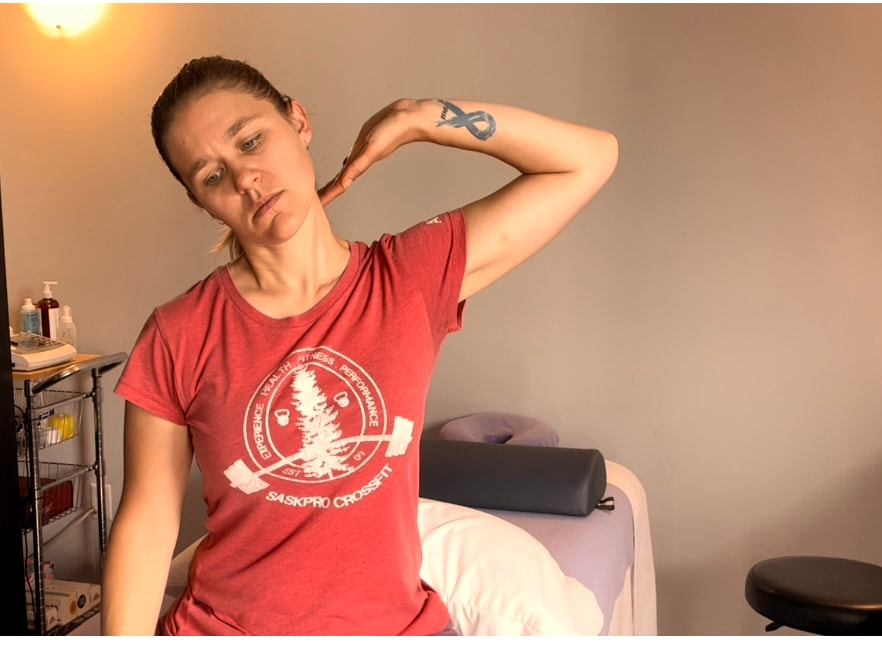
If you tested positive with the nerve tension test….NOW WHAT… Good news you can work on improving neural tension the same way you can work on mobility of a joint or flexibility of a muscle. Check out our YouTube Channel to view our new nerve flossing videos to improve neural tension or book an appointment and receive an in person treatment or virtual guidance. NOTE: Please seek a professional diagnosis and discontinue the tests suggested if you have an increase in symptoms. This is only meant as a guide. We do not diagnosis. Are you suffering from numbness and tingling in your hands and fingers? Do you have general aches in your shoulder, elbow or wrist? This discomfort is often intermittent or moves around. You could describe the pain like a tooth ache but you don’t find that the site itself is tender to the touch. Do you suffer from chronic neck and upper back tightness? You could have a nerve impingement, tension or entrapment. Often times neural tension is diagnosed as carpal tunnel syndrome, tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, or shoulder impingement. If you have been receiving treatment for any of these but have not been getting the results you want try this simple test at home to find out if you have neural tension. Start with an Upper Limb Tension Test. Follow the step by step guide to help determine if could benefit from neural tension treatment as part of your health and fitness routine. Book an Athletic Therapy or Massage Therapy appointment today if you would like to be walked through this testing and receive treatment. Upper Limb Tension Test # 3 - Ulnar Nerve Test
2. Bring your left arm out to the side with the palm facing down and extend the wrist back as you raise your arm to shoulder height 3. As you bring your arm to shoulder height your palm should be facing your cheek and your elbow should be bent. 4. Try on the opposite side. Compare right and left. You could feel tension anywhere between your shoulder and fingers. Tension is usually felt at the pinky side of the hand and forearm. If you tested positive with the nerve tension test….NOW WHAT…
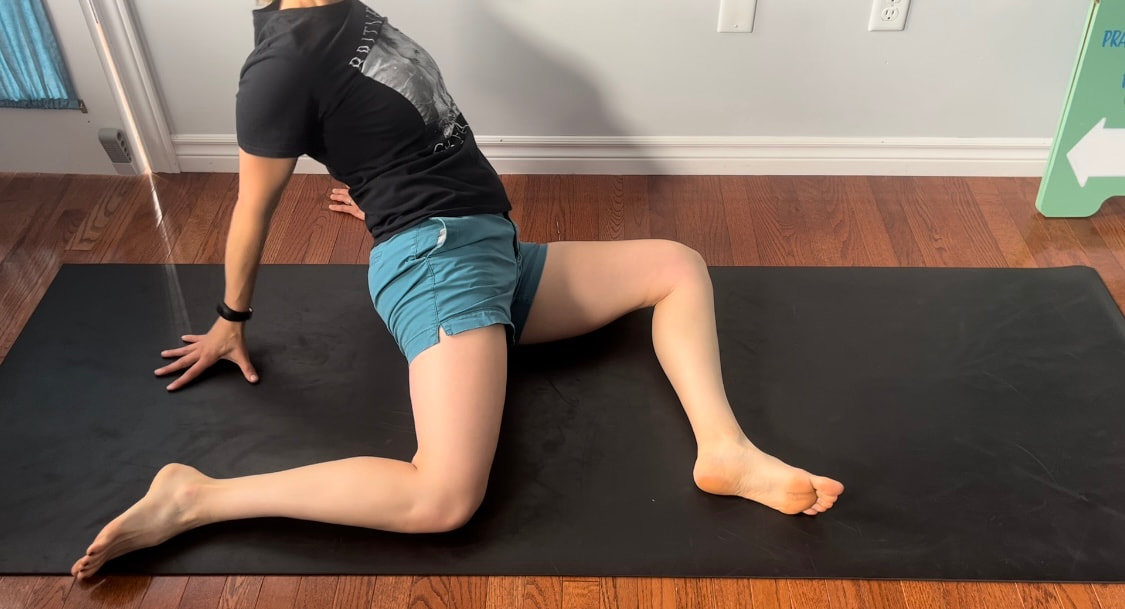
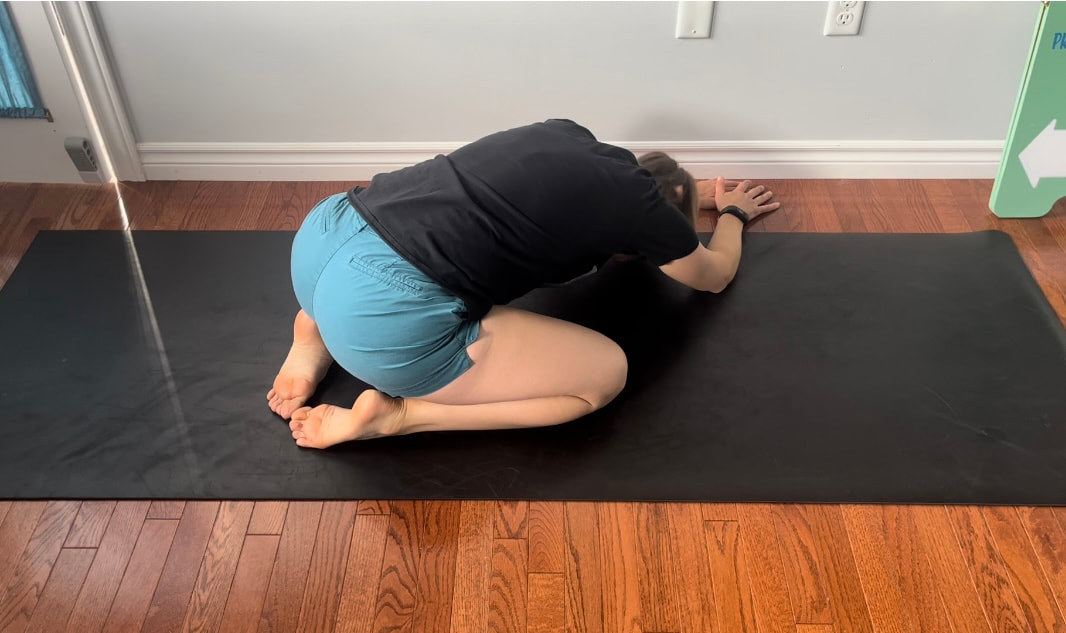
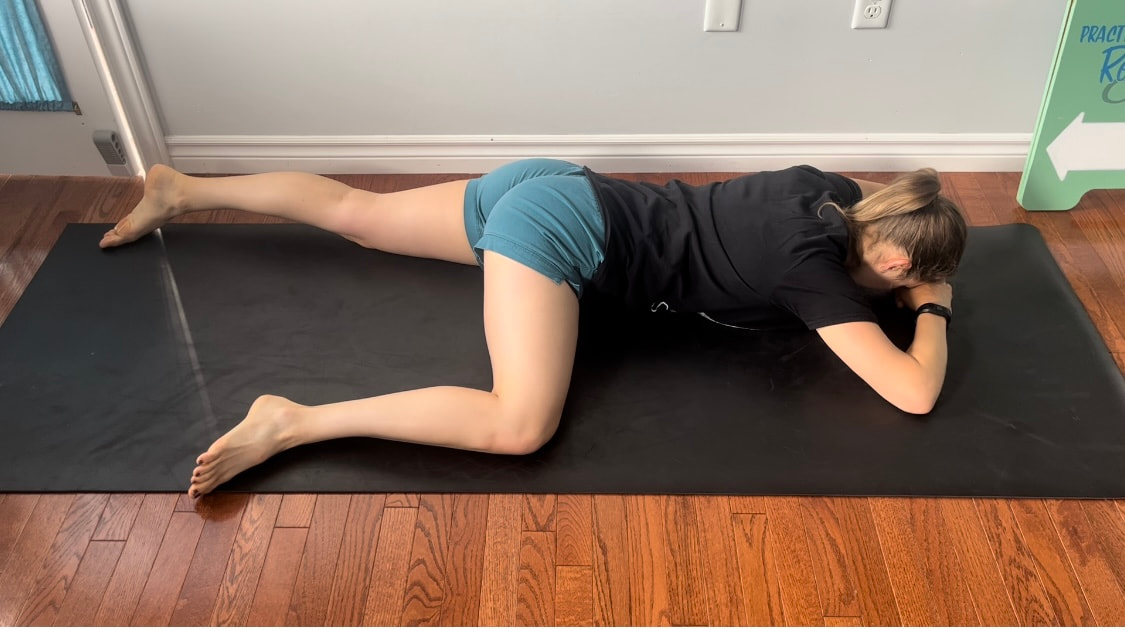
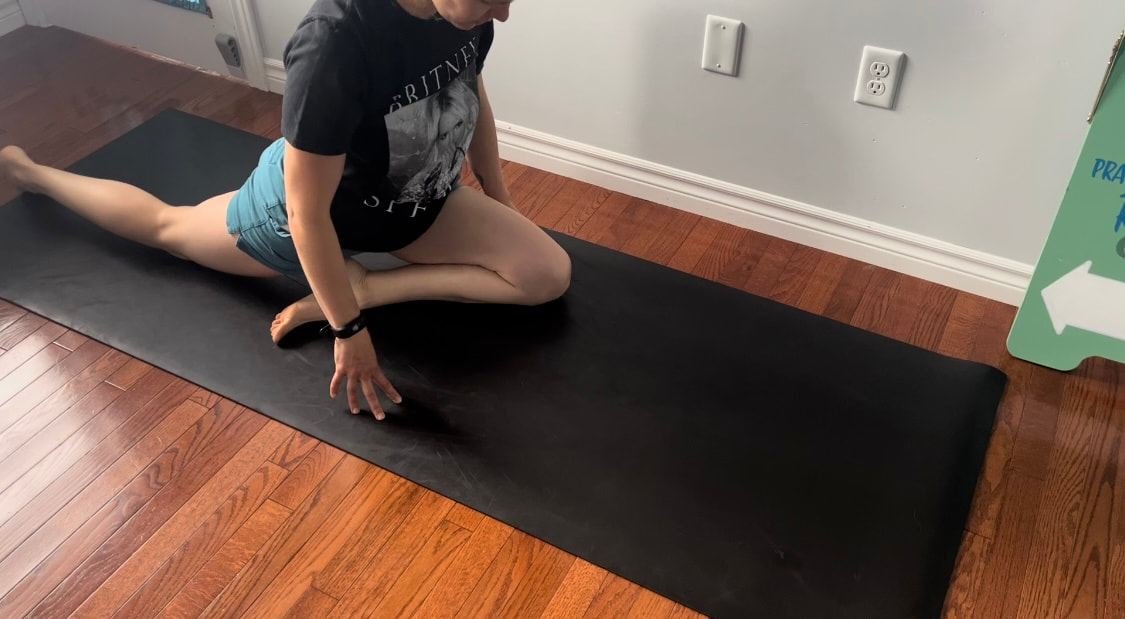
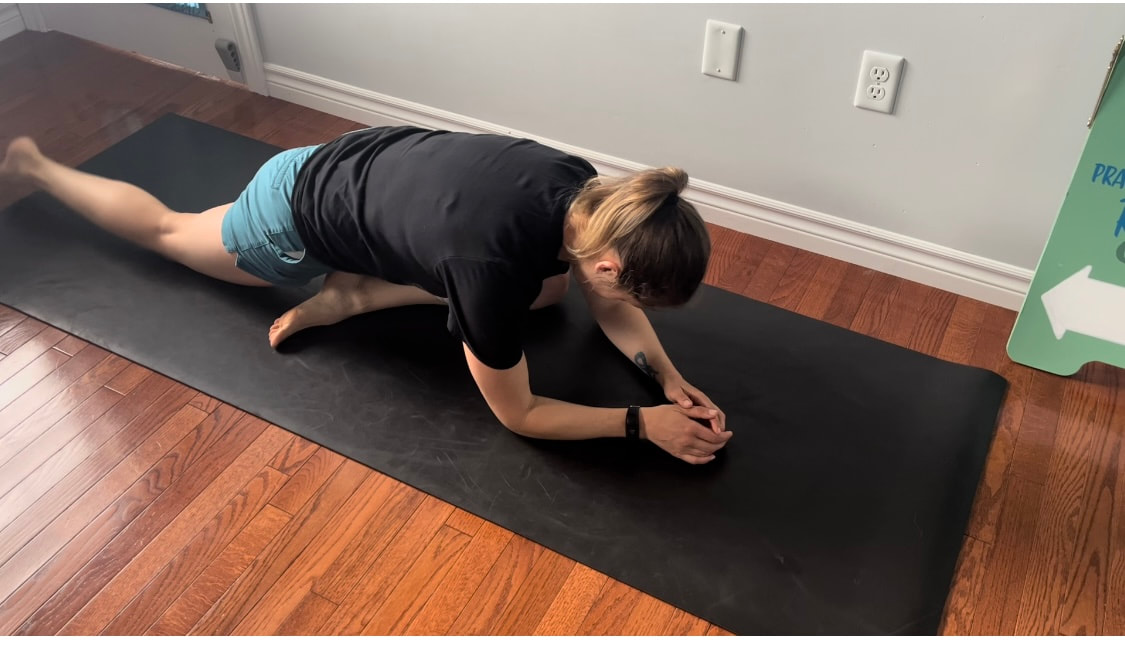
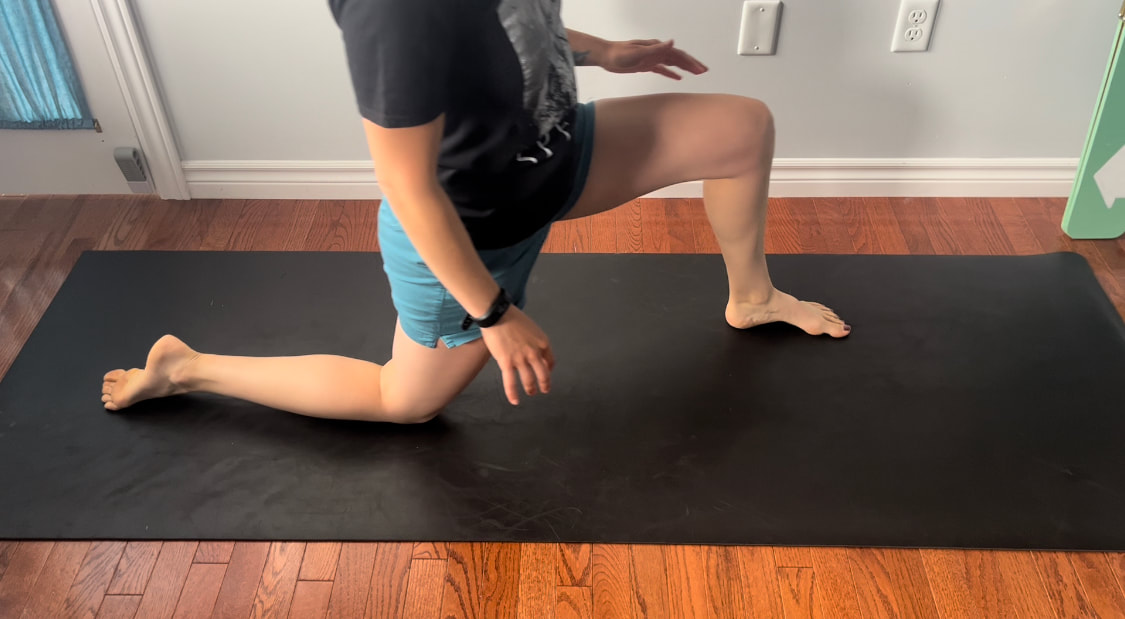
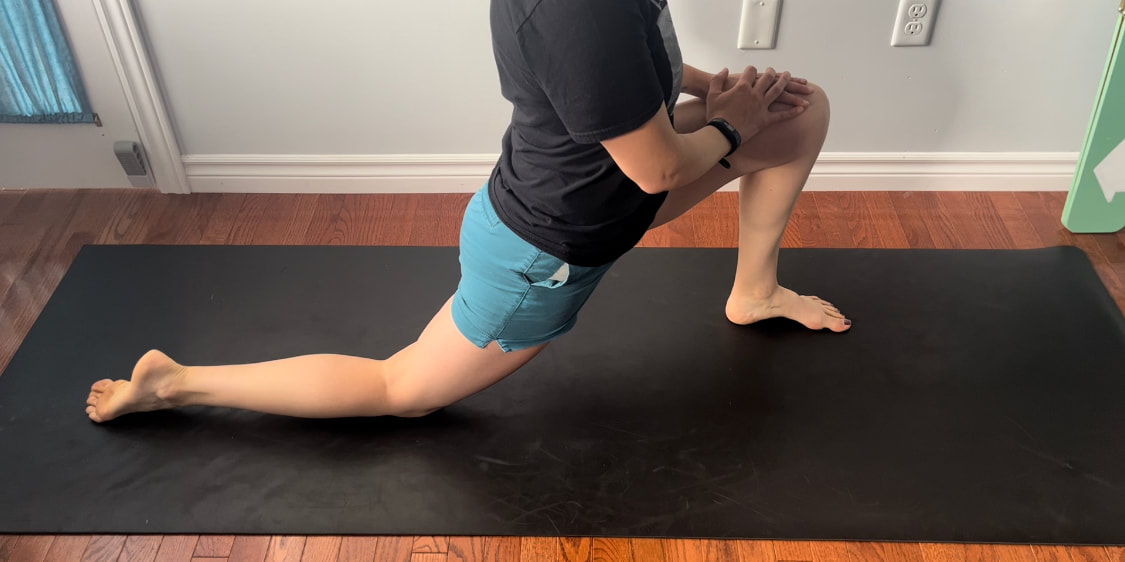
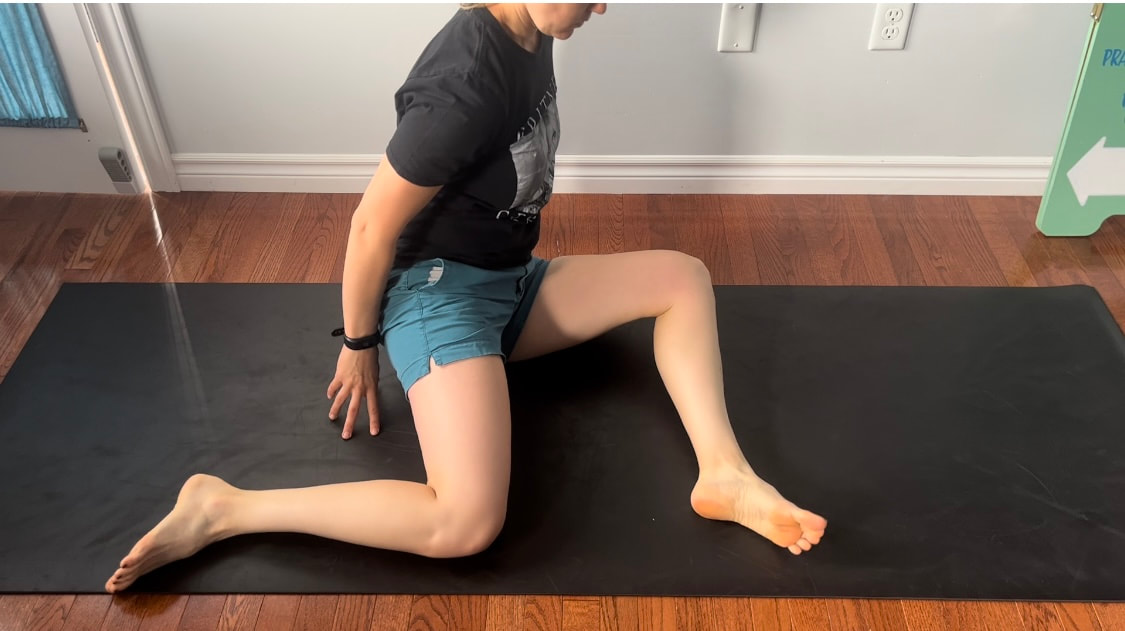
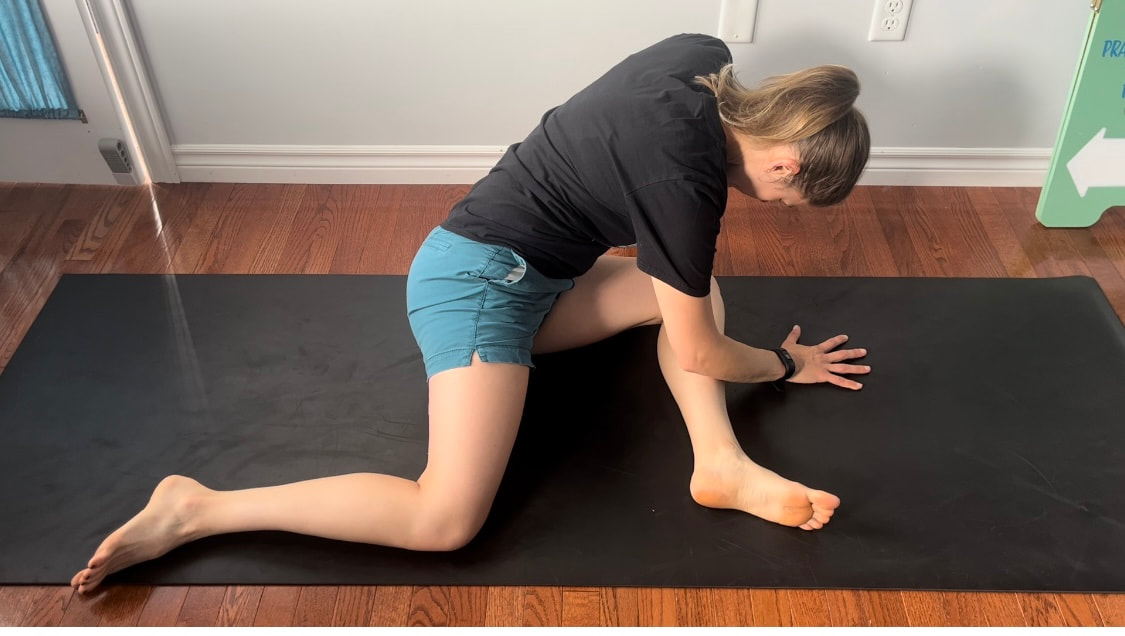
Good news you can work on improving neural tension the same way you can work on mobility of a joint or flexibility of a muscle. Check out our YouTube Channel to view our new nerve flossing videos to improve neural tension or book an appointment and receive an in person treatment or virtual guidance. Suffering from low back and hip pain associated with poor hip mobility. These are 5 of my favorite beginner mobility exercises that will keep you limber and flexible. The videos for each of these exercises will be made available on our YouTube and Instagram/Facebook pages later this month. 1. Deer Pose Starting Position - Begin with your left leg forward, knee bent and left foot positioned in front of the right foot. Your right hip will be inline with your knee bent and your left foot inline with the left knee. Stretch - Extend your upper body back you should feel a stretch in the front of the right leg. Hold for a minimum of 20 seconds. Stretch - Fold forward over the left leg. Hold the stretch for a minimum of 20 seconds. 2. Wide Leg Child’s Pose Starting Position - Start with stretch on your knees sitting back on your feet. Bring your knees wider than hip width apart.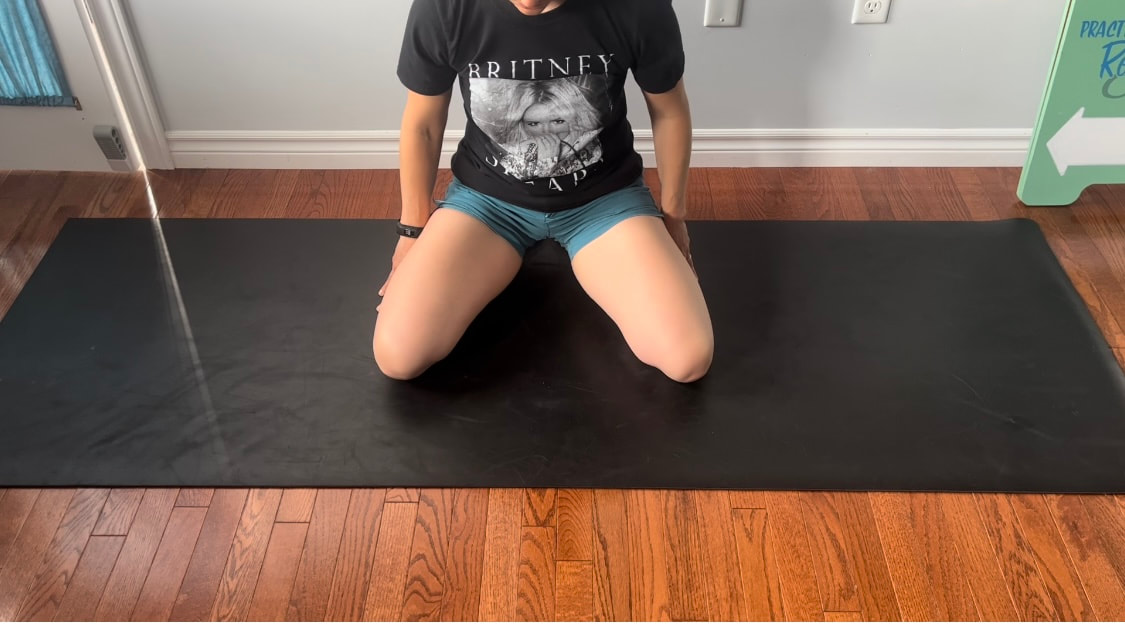  The stretch - Fold forward between your knees reaching your arms over head. Hold for a minimum of 20 seconds 3. Half Frog Pose Lying on your stomach bend your knee bringing it out to your side lining it up with your hip. Keep the right foot inline with the knee hold for a minimum of 20 seconds. 4. Pigeon Stretch Starting position - Begin on your knees. Bring your left shin to the ground and tuck your left foot close to your right hip. Extend your right leg back. Stretch - Fold forward over your left leg. Hold for a minimum of 20 seconds. If its uncomfortable to have your right knee directing on the floor add a pillow for extra comfort. 5. Low Lunge Starting Position - Begin with your right knee down on the ground (or pillow) and your left foot planted in front of you. Stretch - Shift your weight forward bending your left knee. Squeeze your butt to keep your hips from tilting. Hold for a minimum of 20 seconds. Take Care,
Roz |
AuthorRozalind Sorensen Archives
December 2022
Categories |





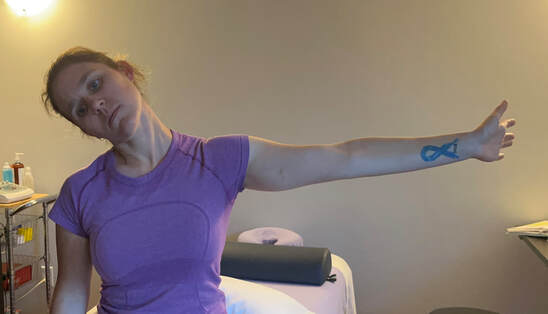













 RSS Feed
RSS Feed