Series 3 - TENS Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulators
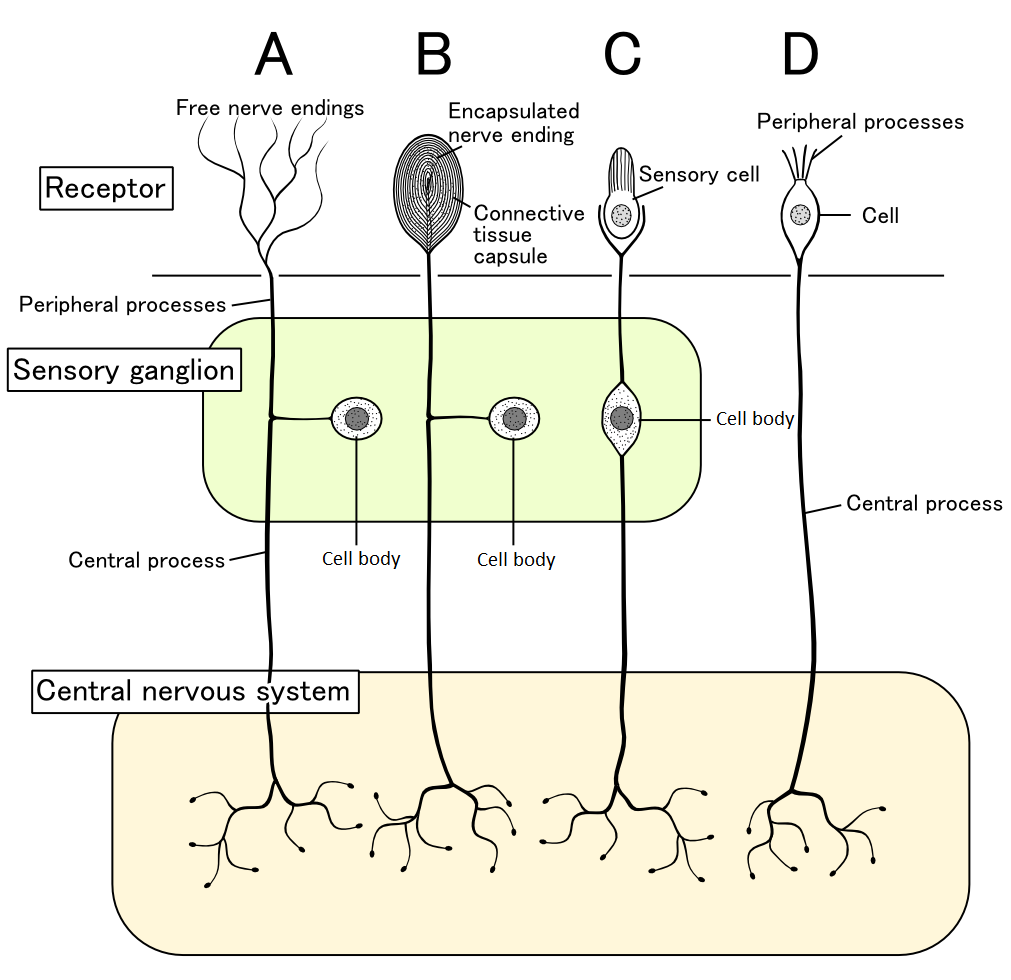
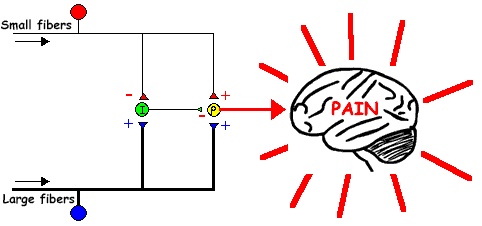
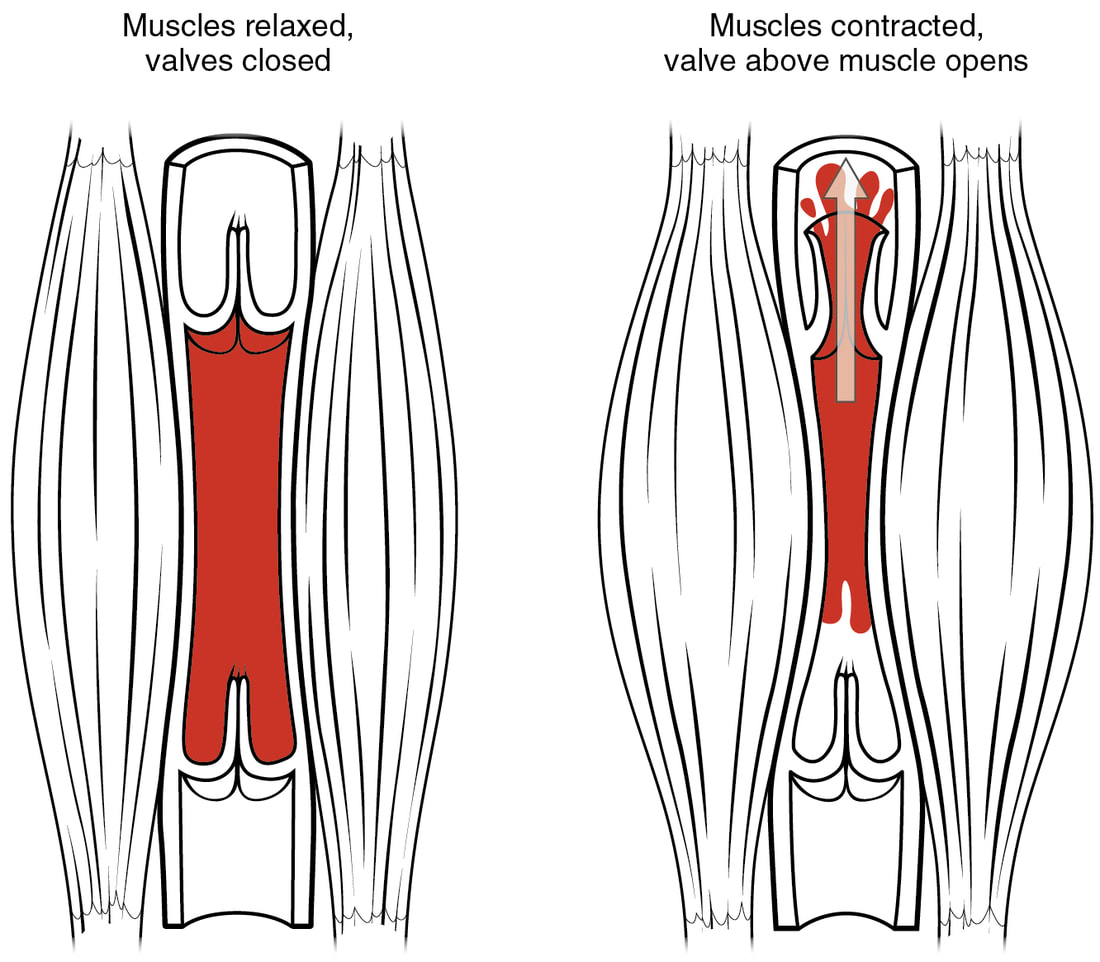
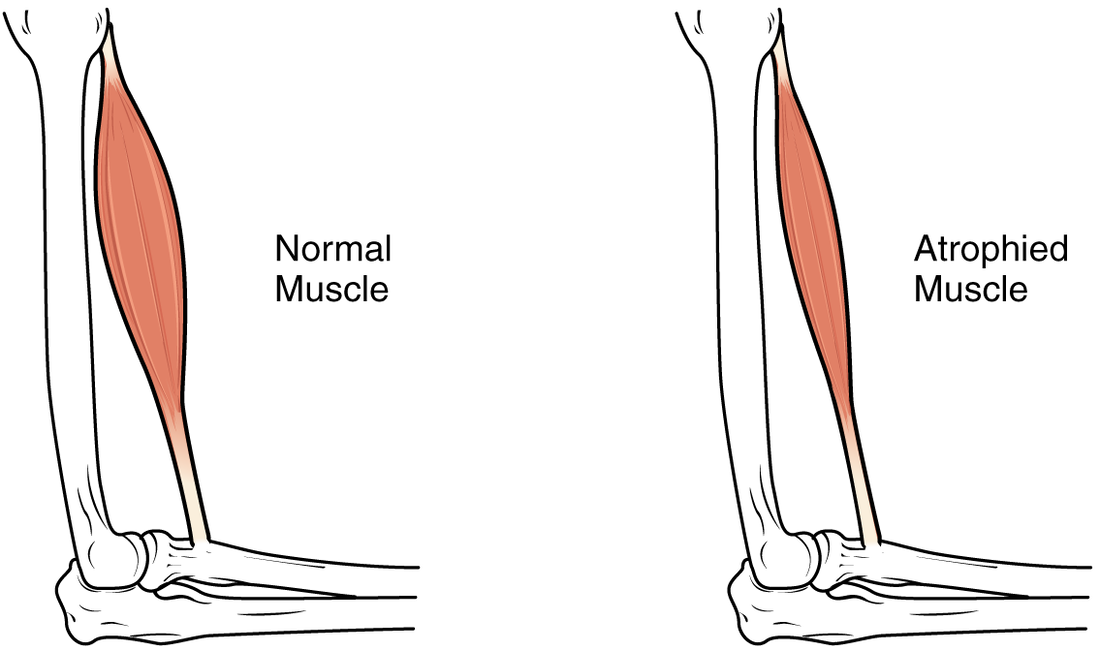
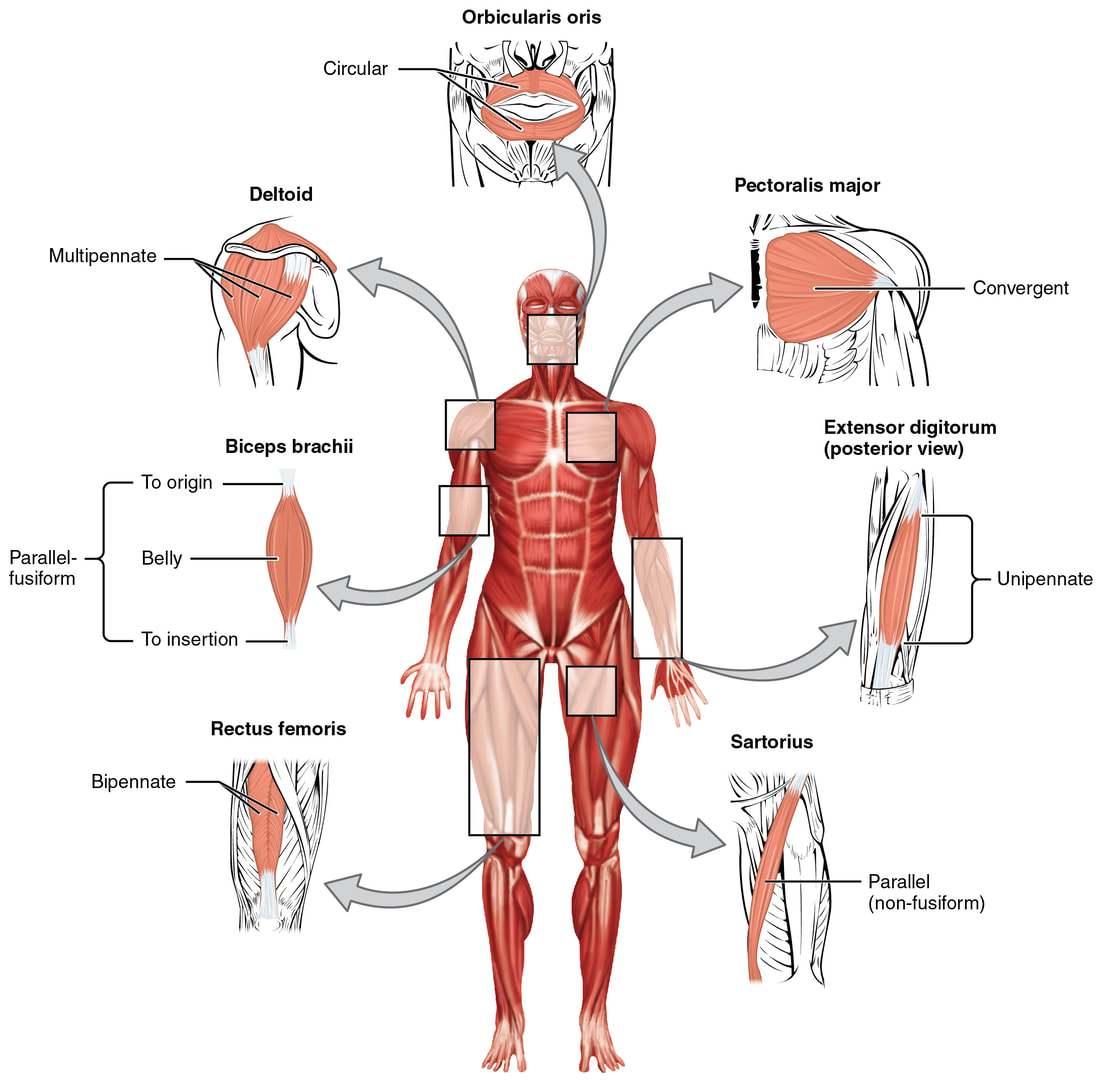
Pain ModulationMuscle ContractionReferences
Arnheim’s Principles of Athletic Training - A Competency Based Approach, William E. Prentice, 12 Edition, 2006, pg 416-420 Upcoming - Series 4 - Massage
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorRozalind Sorensen Archives
December 2022
Categories |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed